|
|

Jinzeng Yang
|
 |
| Affiliation: |
Department of Human Nutrition, Food and Animal Sciences |
| Position: |
Associate Professor |
| Degree: |
PhD (University of Alberta, Canada) |
| Phone: |
(808) 956 6073 |
| Fax: |
(808) 956 4024 |
| Email: |
jinzeng@hawaii.edu |
| Address: |
1955 East West Road, Rm 216, Honolulu, HI 96822 |
|
Research projects:
Molecular regulation of muscular and skeletal formation and development.
Description of research:
The musculoskeletal system originates from the mesoderm during embryo development with major development in the embryonic period and continuous increase in size and complexity in structure in the fetal period. Both muscular and skeletal formations are highly dependent upon sequential switching on and off specific gene activities that control cellular events. The long-term goal of my research programs is to understand the fundamental mechanisms and the critical genes that control skeletal, muscular and adipose tissue formation and development. Our research experiences and technical expertise are at gene expression analysis and transgenic animals, which have been used for defining key regulatory factors and their effects on the musculoskeletal system.
Recent studies indicate that myostatin, a member of TGF-beta superfamily, plays significant roles in the development of musculoskeletal system. Loss of myostatin function by natural mutations is responsible for dramatic muscle mass phenotype in cattle, human and dog. Mice without functional myostatin produce twice the muscle mass of wild-type mice. By inhibiting both myoblast cell proliferation and differentiation, myostatin reduce fiber number during muscle formation. Transgenic mice expressing myostatin propeptide were generated and maintained in my laboratory. As shown in the figure, myostatin propeptide transgene increased growth rate, resulting in 22-44% more muscle mass than wild-type at 9 weeks of age. Our recent data showed that the total mass of the main muscles of transgenic mice increased by 98.8–132.9% compared to wild-type mice at 6 months of age. Muscle histochemistry indicates that the cross-sectional areas of fast-glycolytic fibers are much larger in transgenic mice than that in wild-type mice while fiber number was not different.
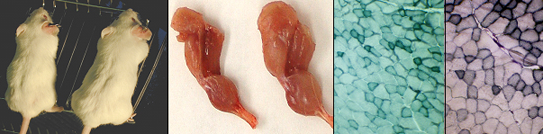
Figure 1. Transgenic mice with over-expressed myostatin propeptide. The transgenic (right) and its littermate non-transgenic littermate control (left) are at 9 weeks of age. The rear leg and histochemistry staining of gastrocnemiuss/plantaris muscle fro transgenic mouse (right) and littermate control are also shown.
Selected publications:
- Zhao B, Li EJ, Wall RJ, Yang J. 2009. Coordinated patterns of gene expression for adult muscle build-up in transgenic mice expressing myostatin propeptide. BMC Genomics. 10:305-315.
- Li Z, Zhao B, Kim YS, Hu CY, Yang J. 2009. Administration of a mutated myostatin propeptide to neonatal mice significantly enhances skeletal muscle growth. Mol. Reprod. Dev. Published online, September 9, 2009.
- Li Z, B. Cao, Zhao B, Yang X, Fan MZ, Yang J. 2009. Decreased expression of calpain and calpastatin mRNA during development are highly correlated with muscle protein accumulation in neonatal pigs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A: Mol. Integrat. Physiol. 152:498-503.
- Laoong-u-thai Y, Zhao B, Phongdara A, Ako H, Yang J. 2009. Identifications of SUMO-1 cDNA and its expression patterns in Pacific white shrimp Litopeanaeus vannamei. Int J Biol Sci. 5:205-14.
- Suzuki,ST, Zhao B, Yang J. 2008. Enhanced muscle by myostatin propeptide increases adipose tissue adiponectin, PPAR-α and PPAR- γ expressions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 369: 767-73.
- Wu Z, Li Z, Yang J. 2008. Transient transgene transmission to piglets by intrauterine insemination of spermatozoa incubated with DNA fragments. Molecular Reproduction and Development 75: 26-32.
- Yang J, Zhao B. 2006. Postnatal expression of myostatin propeptide cDNA maintained high muscle growth and normal adipose tissue mass in transgenic mice fed a high-fat diet. Molecular Reproduction and Development 73:462-469.
- Cesar J, Zhao B, Malecha S, Ako H, Yang J. 2006. Morphological and biochemical changes in the muscle of the marine shrimp litopenaeus vannamei during the molt cycle. Aquaculture 261:688 -694.
- Zhao B, Wall RJ, Yang J. 2005. Transgenic expression of myostatin propeptide prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 337:248-255.
- Yang J, Zhao B, Baracos VE, Kennelly JJ. 2005. Effects of bovine somatotropin on beta-casein mRNA levels in mammary tissue of lactating cows. Journal of Dairy Science. 88: 2806-2812.
- Yang J, Ratovitski T, Brady JP, Solomon MB, Wells KD, Wall RJ. 2001. Expression of Myostatin Pro Domain Results in Muscular Transgenic Mice. Molecular Reproduction and Development 60: 351-361.
|
|



